What is Cholesterol and How to Keep a Proper Balance?
Cholesterol is a vital substance in our bodies that plays a crucial role in various physiological functions. However, an imbalance in cholesterol levels can lead to health complications, particularly cardiovascular diseases. In this article, we will explore what cholesterol is, how to identify high cholesterol levels, foods that can impact cholesterol, and effective ways to manage and improve your cholesterol levels.
What is Cholesterol?
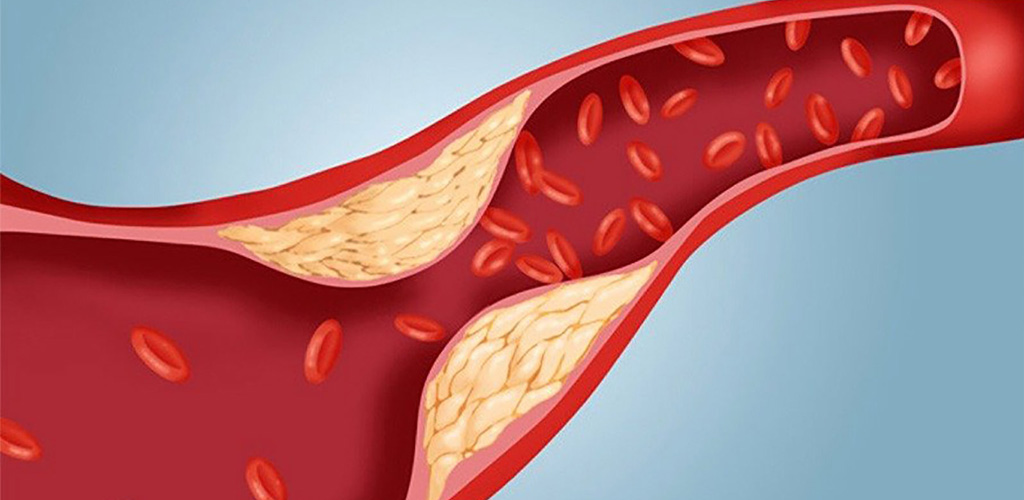
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance found in every cell of the body. It is essential for building cell membranes, producing hormones, and aiding in the digestion of fats. There are two main types of cholesterol: low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL is often referred to as "bad" cholesterol, as high levels can contribute to plaque buildup in arteries, while HDL is considered "good" cholesterol, helping to remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream.
How Do I Know if I Have High Cholesterol?
High cholesterol often goes unnoticed as it doesn't typically present symptoms. The only way to determine cholesterol levels is through a blood test called a lipid panel. This test measures total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. It is recommended to have cholesterol levels checked regularly, especially if you have a family history of heart disease or other risk factors.
What Foods Will Make My High Cholesterol Worse?
Certain dietary choices can contribute to elevated cholesterol levels. Foods high in saturated and trans fats, such as red meat, full-fat dairy products, and processed snacks, can raise LDL cholesterol. Additionally, an excessive intake of refined carbohydrates and sugars may contribute to elevated triglyceride levels, another type of fat found in the blood.
What Foods Will Lower My Cholesterol?
Adopting a heart-healthy diet can positively impact cholesterol levels. Incorporating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and sources of omega-3 fatty acids, like fish, can help lower LDL cholesterol. Foods rich in soluble fiber, such as oats, beans, and lentils, can also contribute to reducing cholesterol absorption in the bloodstream. Plant sterols and stanols, found in certain margarines and fortified foods, may help lower LDL cholesterol as well.
Can Exercise Help to Lower Cholesterol?
Regular physical activity is an essential component of managing cholesterol levels. Exercise can raise HDL cholesterol while helping to lower LDL cholesterol. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week. Activities like brisk walking, jogging, swimming, and cycling are excellent choices for cardiovascular health.
What Are the Risks Linked to High Cholesterol?
High cholesterol is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including coronary artery disease, heart attack, and stroke. When LDL cholesterol levels are elevated, it can lead to the formation of plaques in the arteries, narrowing them and reducing blood flow. These plaques can rupture, causing blood clots that may block blood vessels and result in severe cardiovascular events.
Understanding cholesterol and its impact on cardiovascular health is crucial for maintaining overall well-being. By adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and routine cholesterol screenings, individuals can actively manage and improve their cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart-related complications. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance on cholesterol management and maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle.
Natural Ways to Lower Cholesterol
Focus on Monounsaturated Fats
Including sources of monounsaturated fats in your diet can be beneficial for cholesterol management. Foods like avocados, olive oil, and nuts are rich in monounsaturated fats and can help raise HDL cholesterol while lowering LDL cholesterol.
Prioritize Omega-3s
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and walnuts, have been shown to have positive effects on cholesterol levels. These essential fatty acids can lower triglycerides, reduce inflammation, and contribute to overall heart health.
Limit Trans Fats
Trans fats, often found in processed and fried foods, can significantly raise LDL cholesterol levels while lowering HDL cholesterol. Reading food labels and avoiding products containing partially hydrogenated oils can help reduce trans fat intake.
Eat Soluble Fiber
Soluble fiber is known to lower LDL cholesterol by reducing its absorption in the bloodstream. Foods high in soluble fiber include oats, barley, beans, lentils, fruits, and vegetables. Incorporating these into your diet can contribute to better cholesterol levels.
Avoid Smoking
Smoking not only poses a significant risk to respiratory health but also adversely affects cholesterol levels. Smoking damages blood vessels, making it easier for cholesterol to accumulate and form plaques. Quitting smoking is a crucial step towards improving overall cardiovascular health.
Conclusion
Understanding cholesterol and taking proactive steps to manage it is vital for maintaining a healthy heart. By incorporating natural ways to lower cholesterol into your lifestyle, such as focusing on monounsaturated fats, prioritizing omega-3s, limiting trans fats, eating soluble fiber, and avoiding smoking, you can actively contribute to your cardiovascular well-being. It's essential to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance on maintaining optimal cholesterol levels for a long and healthy life.